Android Partition Manager: How to Partition SD Card
Oct 24, 2025 • Filed to: Mobile Tips & Tactics • Proven solutions
Dr.Fone Basic:
Better Control for Your Phone
Manage, transfer, back up, restore, and mirror your device
Computer, SD card, and mobile phones are places to store files, but the capacity is not enough as you do more of these devices. Then you will plan to partition. So how to Partition SD card for Android?
Part 1: What Is Partition and Android partition manager
A partition is simply a logical division of mass storage or memory into isolated subdivisions. This is normally done to help reduce the burden of the internal storage on the device. In other words, people usually create partitions on the SD Card in order to save more space on the internal storage. Partitioning can help to enhance your disk efficiency. Moreover, it is said that a partition can speed up the Android operating system by a huge margin.
Android Partition Manager
The Android Partition Manager is simply an application that enables you to copy, flash and delete partitions on your Android device. The process of partitioning your SD card helps to free up space and install more programs on your device.

Part 2: Materials and devices required
- Android Gingerbread, Jelly Bean or Ice Cream Sandwich: These are designed to improve speed, extend Android battery life, better application management and improved gaming experience.
- Busy Box: This is a special app that you install on your Android device to give you some additional Linux-based commands. You need to have this app installed since some important commands aren't available and you'll need them for rooting tasks.
- A smartphone
- The MiniTool Partition wizard (can be downloaded online)
- An 8 GB or more Micro SD Card
- Link2SD: This is a handy application that enables you to transfer apps to the SD card. You can use it to manage, list, sort, repair or display applications. If you do not have Link2SD tool, you can install it from the Google Play Store.
- Swapper 2 (for Root users)
Part 3: Operations required before you partition SD card for Android
Backup and format your SD card
First, you are going to format your SD card. So, make sure all the files you currently have saved are backed up in your computer hard drive. Back up only the important files if you don't have adequate free space available.
You can use Dr.Fone - Backup & Restore to backup your Android phone and Android SD card to PC in one click.
Dr.Fone - Backup & Restore (Android)
Flexibly Backup your Android Phone and Android SD Card to PC
- Selectively backup Android data to computer with one click.
- Preview and restore backup to any Android devices.
- Supports 8000+ Android devices.
- There is no data lost during backup, export or restore.
Here are the simple steps to follow:
Step 1. Download and install Dr.Fone. After all is complete, you can then launch it.
Step 2. Simply connect your Android phone to PC and click the Backup & Restore button.
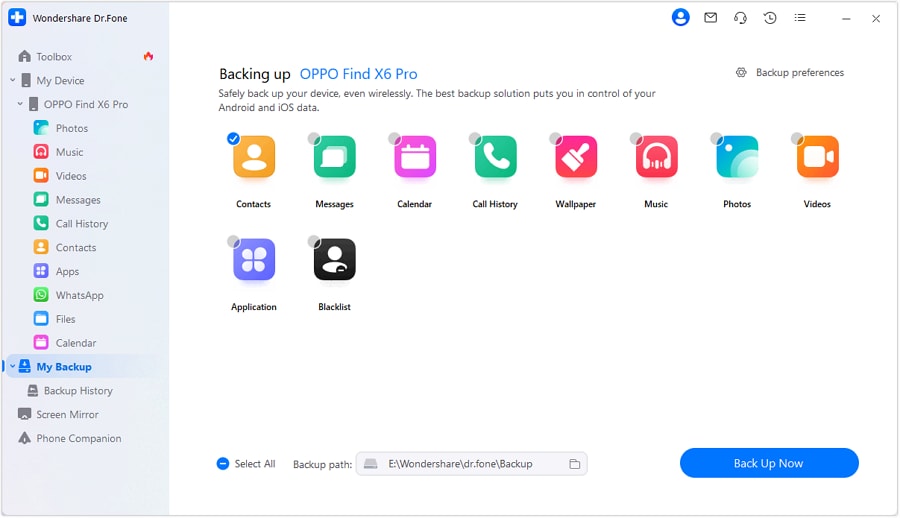
Step 3. A new screen will then be displayed. You can see your phone model name in the upper part. Click "Backup" to continue.
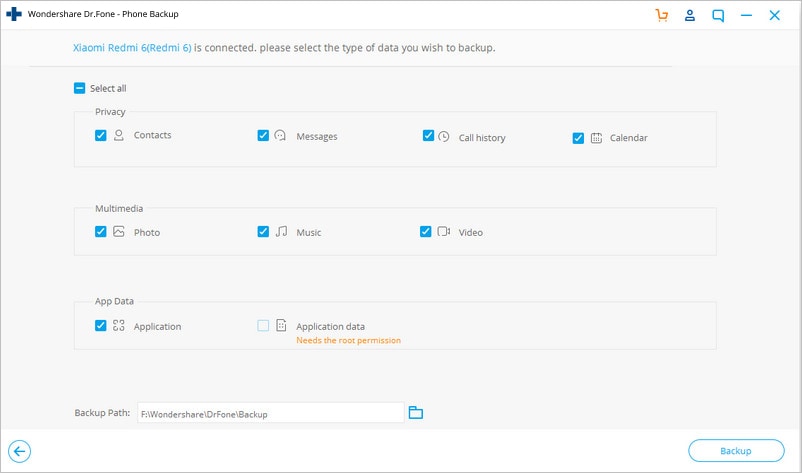
Step 4. Now you can see all the supported file types for backup. Select all the wanted types, specify a storage path that is easy to remember on your computer, and then click "Backup".
With all this done, you can rest assured to format your SD card.
Unlock your bootloader
You now need to unlock your bootloader. For the sake of those who are not familiar with Android bootloader verbiage, let's get some basics out of the way first.
A bootloader is essentially a system designed to instruct the operating system kernel to boot normally. It is usually locked on an Android device because the manufacturer wants to limit you to their Android Operating System version.
With a locked bootloader on your device, it's nearly not possible to flash a custom ROM without unlocking it. Applying force may likely break your device completely beyond repair.
Note: This guide is meant for Android devices with Stock Android OS only such as Google Nexus. Google's Stock Operating System is the kernel of Android without user interface UI alteration.

Step 1: Download and install the Android SDK on your system.
Step 2: Once you have downloaded and installed the SDK, shut down your device and restart it in bootloader mode. Here is how you can do it:
- Nexus One: Press and hold the trackball and power button simultaneously
- Nexus S: Press and hold volume up and power button
- Galaxy Nexus: Press and hold the power button, volume down and volume down at the same time
- Nexus 4: Volume down and power button
- Nexus7: Volume and power simultaneously
- Nexus 10: Volume down, volume up and power button
Step 3: Connect your Android phone or tablet to your PC via a USB and remain patient till all drivers are successfully installed. This usually occurs automatically.
Step 4: Once all the drivers are installed, go to terminal interface on your PC/command prompt and type following command fast-boot oem unlock.
Step 5: Now press enter and your device will show a screen that will alert you about bootloader unlocking. Carefully go through the instructions on the screen and confirm by pressing the volume up button and power button one after the other.
Congratulations! Now you've successfully unlocked the bootloader on your Android device.
Important tips
For Android devices with non-stock Android, you may want to download the unlocking tool from the manufacturer's website. For instance, the HTC official site has a section where you can download an SDK. You only need to know the model of your smartphone.
However, Samsung website does not offer this service, but you can find unlocking tools for Samsung devices. There are also tools you can use to unlock your Sony mobile bootloader.
Again, be sure to install the version intended specifically for your phone model. For LG handset users, unfortunately, there isn't any official section to offer this service. But you can try researching online.
Root your Android
Rooting varies for each device running the Android operating system. It should be noted that this is a very risky process that may destroy or spoil your phone and revoke your warranty. Most phone manufacturing companies take no responsibility if the problem is caused by rooting. Hence, root your smartphone at your own peril.
See how to safely root Android in simple steps. These are the easy-to-follow steps on how to root Android. This way supports most Android models.
But in case that this way does not work on your model, you can try the following rooting method (though it is somewhat more intricate).
Step 1. You will need to download the latest version of SuperOneClick and save it to your laptop or desktop.

Step 2. Connect your Android to your computer.
Note: Never mount the SD card on your computer; the safest method to just have it plugged in. Again, go to the Settings and enable USB debugging.

Step 3. Finally, hit the “Root” button on SuperOneClick. Nevertheless, if your device has a NAND lock, it may fail to unlock. In such cases, click Shell Root button rather than Root button. See the image below.

Step 4. Once you have clicked the Root Button, it may take a while before the process is finished. Once finished, be sure to reboot your device.

Part 4: How to partition SD card for Android
In this tutorial, we will take you step by step through the process of partitioning the SD card for your Android device, so that you can run programs from it.
This is an example of a 16 GB Micro SD card, but you can choose your preferred size as long as it is over 8 GB. Follow all the instructions carefully to avoid any potential problems. Again, this post will not be liable for any inadvertent damages in your phone, Micro SD Card or hardware.
Now have a look at how to do it:
Step 1. First and foremost, connect your SD Card to your PC using an adapter and then open MiniTool Partition Wizard Manager. As said earlier, you can download it online.

Step 2. The SD Card should be showed with five partitions. The only one you need to concentrate on is partition 4 which should be named as FAT32. You will have to resize this partition to your preferred size. This will be the main drive where the Android and the rest of the files will be kept.

Step 3. Select Create as Primary. Determine the size for this partition by factoring out about 32MB for your swap partition and 512MBs for your applications from the maximum size. The 512 partition should be set as an ext4 or ext3. The 32MB partition can be labeled as swap. However, a particular ROM may need a different number apart from 32; thus, always follow whatever is recommended by your ROM developer.

Now that you have all the space of the Micro SD card reserved for one of these 3 partitions, click the “Apply” button and wait for it to finish the process. However, be sure you've set the appropriate file system—FAT32 and Ext2 and both of them formed as PRIMARY.

Wait for it to finish the process.

Step 4. Insert back your SD card to your cell phone and reboot it. Now that you've switched on your phone, go to Google Play Store and download Link2SD. After you have installed the app, you will be prompted to select between ext2, ext3, ext4 or FAT32.In order to work properly, you must choose ext2. The ext2 partition is where your applications will be installed.

Step 5. Once the manuscript has been created, restart your device right way. Open link2SD and if the message does not indicate, it means you are successful. Now go to Link2SD > Settings > Check the auto-link. This is done to automatically move apps after installation to the ext4 partition.



To check your memory, click “Storage Info”. This should show you the existing state of your ext2 partition, FAT3 and internal memory in overall.

Dr.Fone Basic:
Better Control for Your Phone
Manage, transfer, back up, restore, and mirror your device
Android Tips
- Android How-Tos
- 1. Get Out of Android Odin Mode
- 2. Android Keyboard Settings
- 3. Get the Most Memory of Android
- 4. Partition SD Card for Android
- 5. How to Get Snap Score
- 6. Exit Android Factory Mode
- 7. Play MP4 files on Android
- 8. Play WMV on Android Phone
- 9. Reboot your Android Phone
- 10. Turn off Safe Mode on Android
- Android Password Find
- 1. Find Passwords Stored On Android
- 2. See Wi-Fi Password on Android
- 3. Show Wi-Fi Password on Android
- Broken Android Manage
- Data Manage
- 1. Top 3 Android Notification Manager
- 2. Edit Contacts on Android
- 3. Import Contacts from CSV File
- 4. Remove Facebook from Android
- 5. Transfer Phone Contacts to SIM
- 6. Unlock Android with Solid Explorer
- 7. Text from Android to Computer
- 8. Manage Audio on Android Device
- 9. Change System Fonts on Android
- 10. View HEIC File on Android
- Android Tricks



















James Davis
staff Editor